Cybersecurity: How to Stay Safe and Protect Your Business in the Digital Age
Cybersecurity has grown to be a major concern for both individuals and corporations in the digital age. It is more crucial than ever to take precautions to safeguard yourself and your data due to the rising incidence of cyber dangers like data breaches, ransomware attacks, and phishing schemes. We will examine the fundamentals of cybersecurity, several cyber threats, and some best practices for online safety in this article.
What is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is the process of preventing unauthorized access, theft, and damage to computer systems, networks, and data. This covers a wide range of tools, procedures, and methods designed to stop and lessen online dangers. The protection of the confidentiality, integrity, and accessibility of digital information is the aim of cybersecurity.
How Does Cybersecurity Works?
Computer systems, networks, and data are safeguarded using a variety of technologies, procedures, and techniques to prevent unauthorized access, theft, and damage. An overview of how cybersecurity functions are provided below:
- Risk assessment: The first step in cybersecurity is to assess the risks that an organization or individual faces. This involves identifying potential vulnerabilities in computer systems, networks, and data and evaluating the likelihood and potential impact of a cyber-attack.
- Threat detection: Cybersecurity tools and technologies are used to detect potential threats to computer systems, networks, and data. This includes technologies such as firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems that monitor network traffic and scan for suspicious activity.
- Vulnerability management: Cybersecurity measures such as software patching, access controls, and encryption are used to manage vulnerabilities and reduce the risk of exploitation by attackers.
- Incident response: In the event of a cyber attack or security breach, incident response processes are used to contain the damage, investigate the cause of the attack, and restore systems and data to a secure state.
- Training and awareness: Cybersecurity is also about people. Organizations and individuals must be educated on cybersecurity best practices, such as using strong passwords, avoiding phishing scams, and keeping software up to date, to minimize the risk of cyber attacks.
- Continuous monitoring: Cybersecurity is not a one-time event. It requires continuous monitoring and adjustment to stay ahead of evolving threats. Regular security assessments, vulnerability scanning, and penetration testing can help identify new vulnerabilities and ensure that security measures remain effective.
Types of Cyber Threats
Both people and companies need to be aware of the following sorts of cyber threats:
- Malware: Malware refers to any type of malicious software designed to harm computer systems or steal data. Common types of malware include viruses, worms, trojan horses, and ransomware.
- Phishing: Phishing is a type of social engineering attack in which an attacker tries to trick a victim into revealing sensitive information such as passwords or financial data.
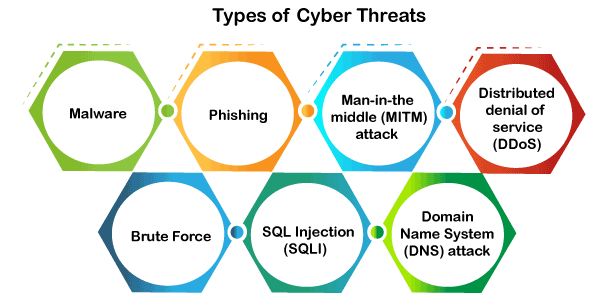
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks: MitM attacks involve intercepting and altering communications between two parties. This can be used to steal sensitive information such as credit card numbers or login credentials.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks: DoS attacks involve flooding a network or website with traffic in order to make it unavailable to users.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): APTs are complex, targeted attacks in which an attacker gains access to a system and remains undetected for a long period of time. This type of attack is often used to steal sensitive information or disrupt operations.
What are the advantages of cybersecurity?

There are several benefits to both individuals and organizations from cybersecurity. Here are a few of the main advantages:
- Protection against cyber threats: The primary advantage of cybersecurity is protection against cyber threats such as data breaches, malware, and phishing attacks. By implementing security measures such as firewalls, antivirus software, and strong passwords, individuals and businesses can reduce their risk of becoming a victim of cybercrime.
- Safeguarding sensitive data: Cybersecurity measures can help safeguard sensitive data such as personal information, financial data, and intellectual property. This is particularly important for businesses that handle sensitive customer data and confidential information.
- Compliance with regulations: Many industries are subject to regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) that require the protection of sensitive data. Implementing cybersecurity measures can help ensure compliance with these regulations.
- Increased trust and reputation: By demonstrating a commitment to cybersecurity, businesses can increase customer trust and improve their reputation. Customers are more likely to do business with companies that take their privacy and security seriously.
- Reduced downtime and costs: Cybersecurity measures can help prevent downtime caused by cyber threats such as malware and denial-of-service attacks. This can reduce costs associated with lost productivity, system repairs, and data recovery.
- Competitive advantage: Businesses that prioritize cybersecurity can gain a competitive advantage by demonstrating their commitment to protecting customer data and maintaining a secure environment. This can be particularly important in industries where security is a top concern, such as finance and healthcare.
Types Of Cybersecurity:
Organizations and individuals can utilize a variety of cybersecurity techniques to safeguard their digital assets against online attacks. Among the prevalent forms of cybersecurity are:
- Network security: Network security involves securing an organization’s computer network from unauthorized access and attacks. It includes measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and virtual private networks (VPNs).
- Application security: Application security involves protecting an organization’s software applications from security threats. It includes measures such as secure coding practices, penetration testing, and web application firewalls.
- Information security: Information security involves protecting an organization’s sensitive information from unauthorized access, disclosure, or theft. It includes measures such as encryption, access controls, and data backup and recovery.
- Endpoint security: Endpoint security involves securing the endpoints of an organization’s network, such as desktops, laptops, and mobile devices. It includes measures such as antivirus software, encryption, and mobile device management.
- Cloud security: Cloud security involves securing an organization’s data and applications in cloud computing environments. It includes measures such as access controls, encryption, and regular auditing and monitoring.
- Internet of Things (IoT) security: IoT security involves securing the network of connected devices that make up the IoT ecosystem. It includes measures such as secure device design, authentication, and data encryption.
- Disaster recovery and business continuity: Disaster recovery and business continuity involve planning and preparing for unforeseen events such as cyber-attacks, natural disasters, and power outages. It includes measures such as data backup and recovery, alternative power sources, and contingency planning.
These are only a few of the typical forms of cybersecurity that businesses and individuals can utilize to safeguard themselves against online dangers. To ensure the strongest possible defense against cyberattacks, it’s crucial to establish a thorough cybersecurity strategy that addresses all potential points of weakness.
Best Practices for Cybersecurity
It’s critical to adhere to cybersecurity best practices if you want to safeguard your personal information and your company from online attacks. Here are a few advice:
- Use strong passwords: Use a unique and complex password for each account, and consider using a password manager to keep track of your passwords.
- Keep software up-to-date: Keep your operating system, web browser, and other software up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates.
- Use two-factor authentication: Enable two-factor authentication for all accounts that support it. This adds an extra layer of security to your login process.
- Backup your data: Regularly back up important data to an external hard drive or cloud storage service.
- Use antivirus software: Install and regularly update antivirus software to protect against malware.
- Educate yourself: Stay informed about the latest cybersecurity threats and best practices by reading news articles and online resources.
Conclusion
In the digital age, cybersecurity is a major problem, and both individuals and businesses need to take precautions to safeguard themselves. You may lower your risk of becoming a victim of cybercrime by adhering to best practices including using strong passwords, updating software, and storing up data. Keep in mind that everyone has a responsibility to keep safe online.

