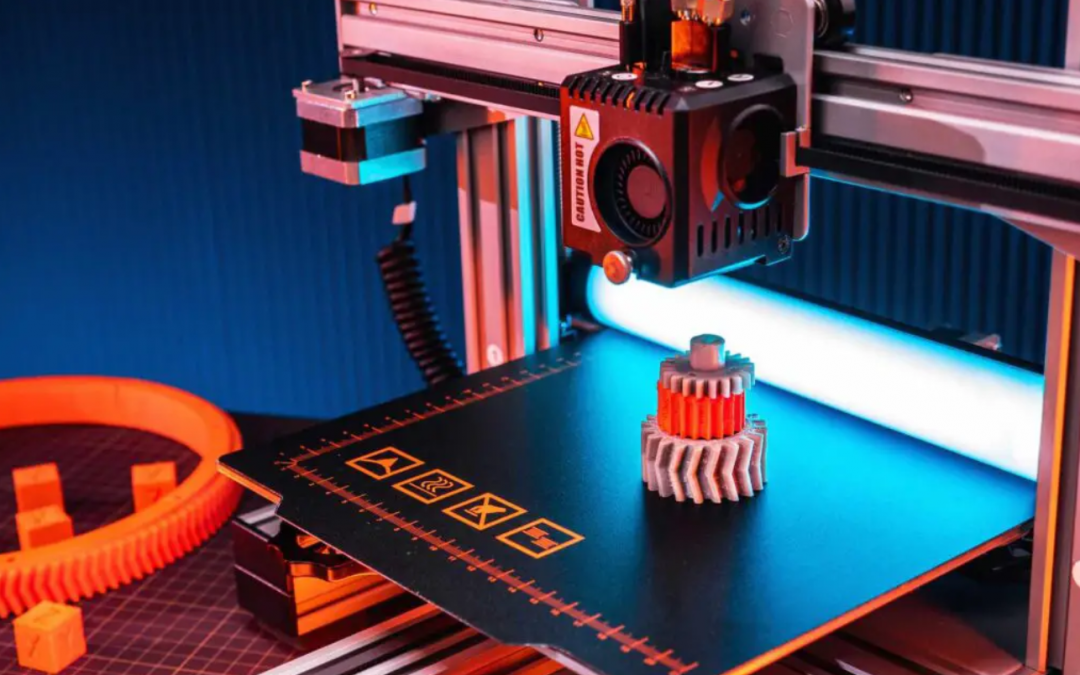
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a revolutionary technology that has transformed the way we design, create and produce physical objects. It has been around for decades, but recent software, hardware, and materials advances have made 3D printing more accessible and affordable than ever before. In this article, we will explore what 3D printing is, how it works, and its applications in various industries.
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing is a process of creating three-dimensional objects from digital designs. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, which involve subtracting material from a block or sheet of material, 3D printing adds material layer by layer until the object is complete. This process is also known as additive manufacturing because it involves adding material rather than subtracting it.

How does 3D Printing Work?
3D printing begins with a digital design created using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software. This design is then converted into a format that can be read by a 3D printer. The printer then uses this design to create the object layer by layer.
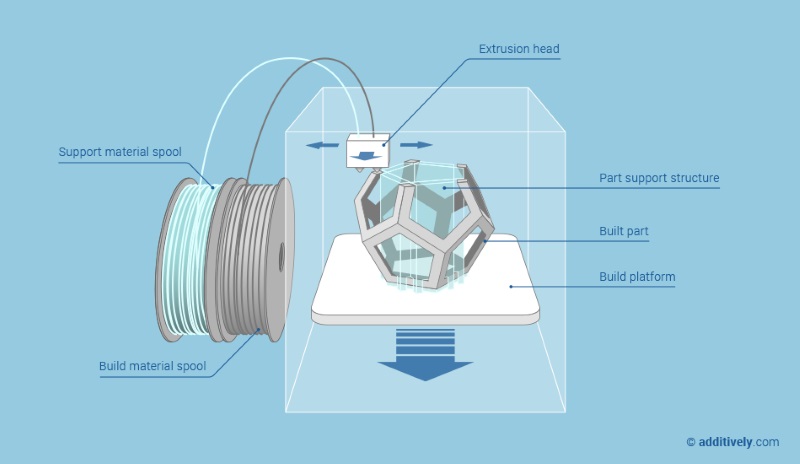
There are several types of 3D printing technologies, including Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). Each technology uses a different method of adding material, and the choice of technology depends on the type of material being used and the desired properties of the final product.
What are the advantages of 3D printing?
One of the biggest advantages of 3D printing is its ability to create complex geometries that are difficult or impossible to manufacture using traditional manufacturing methods. 3D printing also allows for rapid prototyping, which means that designers can quickly create and test multiple iterations of a design before settling on a final version. Additionally, 3D printing reduces waste and is more environmentally friendly than traditional manufacturing methods, as it only uses the amount of material needed to create the object.
Applications of 3D Printing
3D printing has numerous applications across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, healthcare, architecture, and education. Here are some of the most common applications of 3D printing:
- Prototyping: 3D printing is often used to create prototypes of products before they are mass-produced. This allows designers and engineers to test and refine their designs before investing in expensive manufacturing equipment.
- Manufacturing: 3D printing is also used in small-batch manufacturing, where it is more cost-effective than traditional manufacturing methods. This is particularly useful for creating custom-made or one-of-a-kind products.
- Healthcare: 3D printing is being used to create medical implants, prosthetics, and even human organs. This technology has the potential to revolutionize healthcare by making personalized treatments more accessible.
- Education: 3D printing is increasingly being used in classrooms to teach students about design, engineering, and manufacturing. It allows students to bring their ideas to life and provides a hands-on learning experience.
Challenges of 3D Printing
While 3D printing has many advantages, there are also some challenges that must be addressed. One of the biggest challenges is the limited range of materials that can be used in 3D printing. While there are many materials available, the range is still limited compared to traditional manufacturing methods. Additionally, the quality of 3D-printed objects can be lower than that of traditionally manufactured objects, particularly when it comes to strength and durability.
What is the future of 3D printing?
As 3D printing technology continues to advance, it is expected to have a significant impact on the future of manufacturing. It has the potential to revolutionize supply chains by allowing for decentralized manufacturing, where products can be created on-site rather than being transported from a central location. 3D printing could also lead to a more sustainable future by reducing waste and energy consumption in the manufacturing process. Additionally, 3D printing has the potential to transform the healthcare industry by allowing for personalized medical devices and drugs.
Conclusion
Overall, 3D printing is a rapidly evolving technology with the potential to revolutionize how we design, create, and produce physical objects. It has numerous applications across various industries and is increasingly being used in education. While there are still challenges that must be addressed, the potential benefits of 3D printing are significant, and it is an exciting technology to watch in the coming years.

