Edge computing is a relatively new paradigm in the field of computing that has gained increasing attention in recent years. It involves processing data closer to the source of its creation, rather than sending it to a centralized cloud or data center for processing. This approach offers several advantages over traditional cloud computing, including reduced latency, improved reliability, and increased security.
What is Edge Computing?
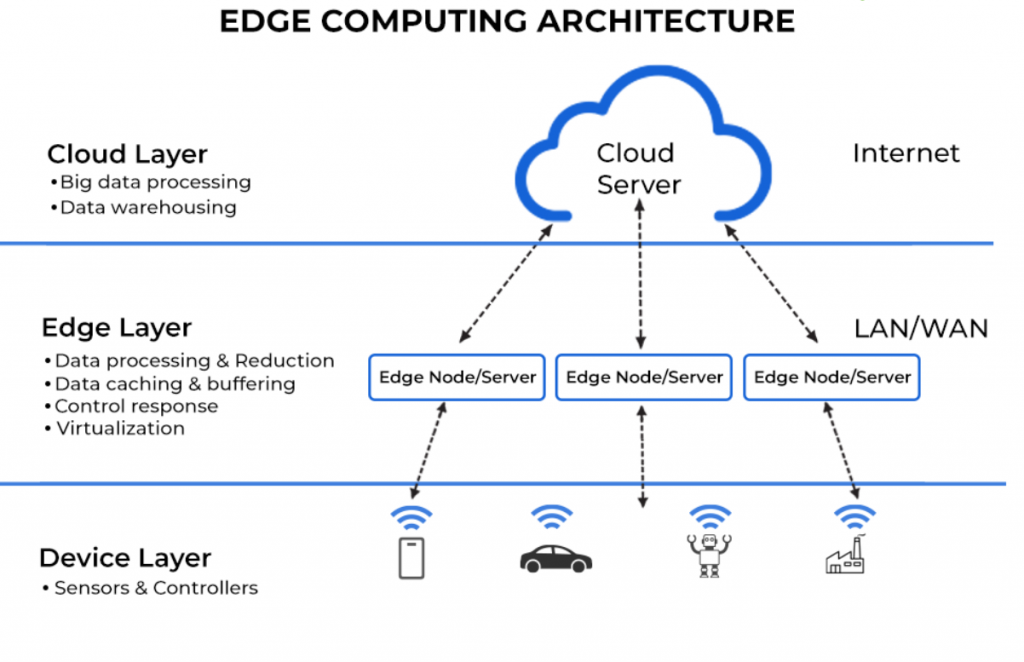
Edge computing refers to a distributed computing architecture that moves the processing of data from centralized servers to devices closer to the source of the data. The term “edge” refers to the network edge, which is the point at which devices connect to the internet. In an edge computing environment, data is processed locally on edge devices, such as smartphones, tablets, IoT devices, and other edge devices, rather than being sent to a remote data center.
Edge computing architectures are designed to address the challenges of processing large volumes of data generated by IoT devices in real time. With IoT devices, data is created at the edge of the network, and as a result, it is more efficient to process it locally, rather than sending it to a central server for processing.
Benefits of Edge Computing
There are several benefits of edge computing that make it an attractive approach for organizations that need to process large amounts of data. Some of these benefits include:
- Reduced Latency: By processing data at the edge of the network, edge computing can significantly reduce the time it takes for data to travel from the device to the data center and back. This reduces latency, making it possible to process data in real time, which is critical for applications that require immediate decision-making.
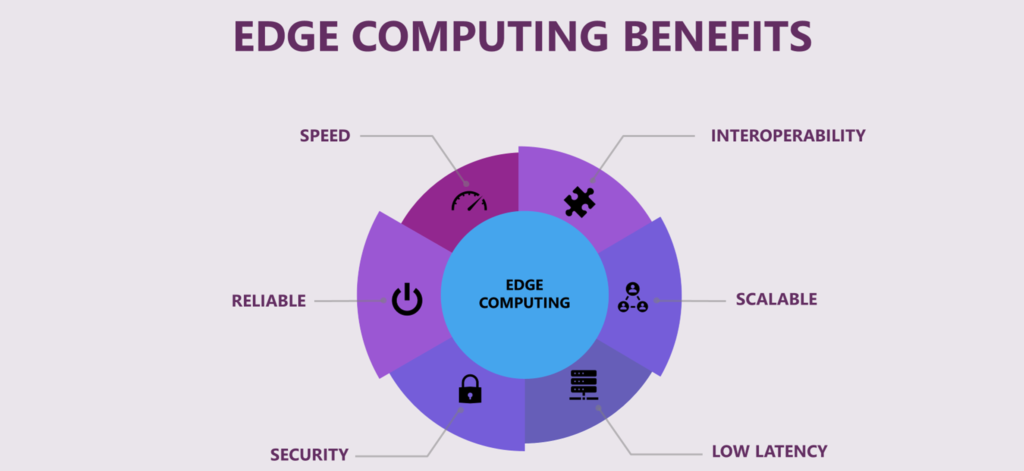
- Improved Reliability: Edge computing can improve the reliability of applications by reducing the dependence on a centralized data center. In a traditional cloud computing environment, if the data center goes down, the entire system is affected. In contrast, edge computing allows devices to continue functioning even if the central data center is offline.
- Increased Security: Edge computing can improve the security of applications by reducing the amount of data that is transmitted over the network. By processing data locally, edge computing reduces the risk of data breaches and other security threats.
- Cost Savings: Edge computing can also reduce the cost of data processing by eliminating the need for expensive data center infrastructure. This can be particularly beneficial for organizations that generate large volumes of data and need to process it quickly.
Challenges of Edge Computing
While edge computing offers many benefits, there are also several challenges that organizations need to be aware of when implementing this approach. Some of these challenges include:
- Complexity: Edge computing environments are inherently more complex than traditional cloud computing environments. This is because they involve a distributed network of devices that need to be managed and monitored.
- Scalability: Scalability can be a challenge in edge computing environments, as it can be difficult to add new devices to the network and ensure that they are properly configured and integrated.
- Security: While edge computing can improve security, it also introduces new security risks. With data being processed locally, it is more vulnerable to physical attacks, and it can be more challenging to monitor and secure the network.
- Maintenance: Maintenance can also be a challenge in edge computing environments, as devices are often located in remote or hard-to-reach locations. This can make it difficult to perform maintenance tasks, such as software updates and hardware repairs.
Examples of Edge Computing Applications
Edge computing has numerous real-world applications, some of which are:
- Autonomous Vehicles: Edge computing can enable autonomous vehicles to process large amounts of data from sensors, cameras, and other sources in real-time, without relying on cloud-based computation. By performing computation closer to the edge of the network, autonomous vehicles can improve their responsiveness and reduce the risk of accidents.
- Industrial Automation: Edge computing can be used to monitor and control industrial processes, such as manufacturing, oil and gas drilling, and power generation. By processing data locally, edge computing can improve the efficiency and reliability of these processes, while reducing the latency and bandwidth requirements.
- Smart Grids: Edge computing can be used to manage and optimize the distribution of energy in smart grids. By processing data from sensors and other sources in real time, edge computing can improve the reliability and efficiency of the grid, while reducing the risk of blackouts and other disruptions.
- Healthcare: Edge computing can be used to monitor and analyze patient data in real time, enabling healthcare providers to provide more personalized and responsive care. By processing data locally, edge computing can also improve the privacy and security of patient data.
- Retail: Edge computing can be used to personalize the shopping experience for customers, by analyzing their preferences and behavior in real time. By processing data locally, edge computing can also improve the responsiveness and reliability of retail applications, such as inventory management and supply chain optimization.
- Smart Homes: Edge computing can be used to automate and optimize the control of smart home devices, such as thermostats, lighting, and security systems. By processing data locally, edge computing can improve the responsiveness and reliability of these devices, while reducing the latency and bandwidth requirements.
- Gaming: Edge computing can be used to enable real-time gaming applications, by processing data from multiple players in real time. By processing data closer to the edge of the network, edge computing can improve the responsiveness and reduce the latency of these applications.
Conclusion
Edge computing is a new paradigm in computing that offers many benefits over traditional cloud computing. By processing data locally, edge computing can reduce latency, improve reliability, increase security, and reduce costs. However, implementing edge computing also introduces new challenges, including complexity, scalability, security, and maintenance.

